This article is more than one year old. Older articles may contain outdated content. Check that the information in the page has not become incorrect since its publication.
Dubbo Basic Usage - Dubbo Consumer Configuration
Dubbo Consumer Configuration
Consumer Configuration Detailed
There are 3 ways to configure the Dubbo Consumer: XML configuration, API call mode configuration, and annotation mode configuration.
XML Configuration
Example of the simplest configuration:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
Xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
Xmlns:dubbo="http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo"
Xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd http://dubbo.apache.org/schema /dubbo http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd">
<dubbo:application name="hello-world-app" />
<dubbo:registry address="multicast://224.5.6.7:1234" />
<dubbo:protocol name="dubbo" port="20880" />
<dubbo:reference id="demoServiceRemote" interface="com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService" />
</beans>
For the supported configuration tags and corresponding configuration items, refer to the usage in the provider.
Next, focus on the configuration of <dubbo:reference/>.
- <dubbo:reference/> List of main attributes supported:
| Property Name | Description |
|---|---|
| id | service reference id, as java bean id, requires unique |
| Interface | interface name for finding services |
| version | version number, consistent with the service provider’s version |
| timeout | service method call timeout (ms) |
| retries | The number of retry attempts by the remote service, excluding the first call, no need to retry, please set to 0 |
| Connections | For each provider’s maximum number of connections, rmi, http, hessian, etc. The short connection protocol indicates the number of restricted connections, and the dubbo equal-length connection association indicates the number of long connections established |
| Loadbalance | Load balancing policy, optional values: random, roundrobin, leastactive, respectively: random, polling, least active call |
| async | Whether to execute asynchronously, unreliable asynchronous, just ignore return value, do not block execution thread |
| generic | generalized call, can bypass |
| check | Check if the provider exists at startup, true error, false ignore |
| Actives | Maximum concurrent calls per method per service consumer |
For other configuration properties, please refer to xsd: http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd
- <dubbo:method/> As a child of <dubbo:reference/>, it can be configured for methods. The more commonly used attributes are:
| Property Name | Description |
|---|---|
| executes | request ceiling for service execution |
| retries | Timeout retries |
| timeout | call timeout |
| Loadbalance | Load balancing policy, optional values: random, roundrobin, leastactive, respectively: random, polling, least active call |
| async | Whether to execute asynchronously, unreliable asynchronous, just ignore return value, do not block execution thread |
| Actives | Maximum concurrent call limit per service consumer |
For other properties, you can refer to xsd above.
Configured coverage relationship
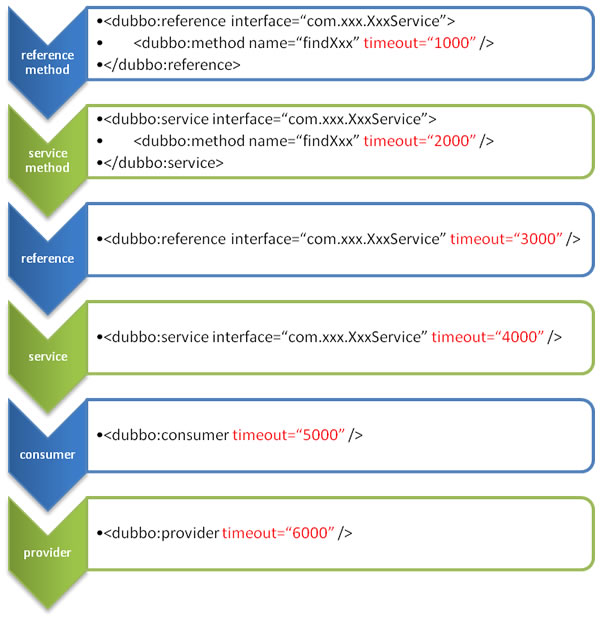
Coverage diagram for configuration
It contains the configuration of the consumer side and the provider, pay attention to the distinction.
annotation
Reference Annotation Remote Service
Public class AnnotationConsumeService {
@com.alibaba.dubbo.config.annotation.Reference
Public AnnotateService annotateService;
// ...
}
The configuration in this way is the same as the previous configuration in xml.
To specify the way dubbo scans the path, refer to the implementation of the provider in the previous section.
api direct trigger
Import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.config.ApplicationConfig;
Import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.config.RegistryConfig;
Import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.config.ConsumerConfig;
Import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.config.ReferenceConfig;
Import com.xxx.XxxService;
// current application configuration
ApplicationConfig application = new ApplicationConfig();
application.setName("yyy");
// Connect to the registry configuration
RegistryConfig registry = new RegistryConfig();
registry.setAddress("10.20.130.230:9090");
registry.setUsername("aaa");
registry.setPassword("bbb");
// Note: ReferenceConfig is a heavy object that internally encapsulates the connection to the registry and the connection to the service provider.
// reference remote service
ReferenceConfig<XxxService> reference = new ReferenceConfig<XxxService>(); // This instance is heavy, encapsulates the connection to the registry and the connection to the provider, please cache it yourself, otherwise it may cause memory and connection leaks.
reference.setApplication(application);
reference.setRegistry(registry); // Multiple registries can use setRegistries()
reference.setInterface(XxxService.class);
reference.setVersion("1.0.0");
// Use xxxService like local beans
XxxService xxxService = reference.get();
methodSpecial settings
// Method level configuration
List<MethodConfig> methods = new ArrayList<MethodConfig>();
MethodConfig method = new MethodConfig();
method.setName("createXxx");
method.setTimeout(10000);
method.setRetries(0);
Methods.add(method);
// reference remote service
ReferenceConfig<XxxService> reference = new ReferenceConfig<XxxService>(); // This instance is heavy, encapsulates the connection to the registry and the connection to the provider, please cache it yourself, otherwise it may cause memory and connection leaks.
...
reference.setMethods(methods); // Set method level configuration
Consumer Calling Remote Service
The above chapters are more from a configuration point of view, and then through a complete example, explain the complete use of dubbo consumer.
There is only one service UserReadService in this example, there is a method getUserById. Need to call a remote service through Dubbo. The specific steps are as follows:
- Create a project If there is already a project, you can ignore it. Create a spring boot project that can be created at https://start.spring.io/. The provider of the service has been defined in the provider section.
- Call the service
@RestController
Public class UserTestController{
@Autowired
Private UserReadService userReadService;
@RequestMapping("/user/getById")
Public String getUserById(Long id){
// just test
Return userReadService.getUserById(id).toString();
}
}
3.Dubbo configuration
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
Xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
Xmlns:dubbo="http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo"
Xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd http://dubbo.apache.org/schema /dubbo http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd">
<dubbo:application name="hello-world-app" />
<dubbo:registry address="multicast://224.5.6.7:1234" />
<dubbo:protocol name="dubbo" port="20880" />
<dubbo:reference id="userReadService" interface="com.package.UserReadService"check="false" />
</beans>
Other ways of configuring Dubbo can refer to the relevant configuration in the previous section, or use the integrated dubbo spring boot starter mode.
