Nacos
1 precondition
- Understand Dubbo basic development steps
- Install and start Nacos service
When Dubbo uses
3.0.0and above, it needs to use Nacos2.0.0and above.
2 Instructions for use
Check here full sample code
2.1 Add dependencies
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.dubbo</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo</artifactId>
<version>3.0.9</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.nacos</groupId>
<artifactId>nacos-client</artifactId>
<version>2.1.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Introduce Dubbo Nacos extension, or you can add Nacos dependency directly as shown above-->
<!--
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.dubbo</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo-registry-nacos</artifactId>
<version>3.0.9</version>
</dependency>
-->
</dependencies>
Add Dubbo and Nacos dependencies
Dubbo
3.0.0and above require nacos-client2.0.0and above
2.2 Configure and enable Nacos
# application.yml (Spring Boot)
dubbo
registry
address: nacos://localhost:8848
or
# dubbo.properties
dubbo.registry.address=nacos://localhost:8848
or
<dubbo:registry address="nacos://localhost:8848" />
To enable the app, see what it looks like after registration or how it works, see [How it works](#4-How it works).
3 Advanced configuration
3.1 Authentication
# application.yml (Spring Boot)
dubbo
registry
address: nacos://localhost:8848?username=nacos&password=nacos
or
# dubbo.properties
dubbo.registry.address: nacos://nacos:nacos@localhost:8848
3.2 Custom namespace
# application.yml (Spring Boot)
dubbo:
registry:
address: nacos://localhost:8848?namespace=5cbb70a5-xxx-xxx-xxx-d43479ae0932
or
# application.yml (Spring Boot)
dubbo:
registry:
address: nacos://localhost:8848
parameters.namespace: 5cbb70a5-xxx-xxx-xxx-d43479ae0932
3.3 Custom grouping
# application.yml
dubbo:
registry:
address: nacos://localhost:8848
group: dubbo
If not configured, the group is specified by Nacos by default. Group and namespace represent different isolation levels in Nacos. Generally speaking, namespace is used to isolate different users or environments, and group is used to further group data in the same environment.
3.4 Register interface-level consumers
After Dubbo3.0.0, the parameter of whether to register consumers is added. If you need to register consumers to the nacos registration center, you need to set the parameter (register-consumer-url) to true, and the default is false.
# application.yml
dubbo:
registry:
address: nacos://localhost:8848?register-consumer-url=true
or
# application.yml
dubbo:
registry:
address: nacos://localhost:8848
parameters.register-consumer-url: true
3.5 More configurations
| Parameter name | Chinese description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
| username | username to connect to Nacos Server | nacos |
| paasword | password to connect to Nacos Server | nacos |
| backup | backup address | null |
| namespace | Namespace ID | public |
| group | group name | DEFAULT_GROUP |
| register-consumer-url | Whether to register the consumer side | false |
| com.alibaba.nacos.naming.log.filename | initialization log file name | naming.log |
| endpoint | Connect to the connection point specified by Nacos Server, please refer to documentation | empty |
| endpointPort | Connect to the connection point port specified by Nacos Server, you can refer to documentation | empty |
| endpointQueryParams | endpoint query parameter query | null |
| isUseCloudNamespaceParsing | whether to parse namespace parameters in the cloud environment | true |
| isUseEndpointParsingRule | whether to enable endpoint parameter rule parsing | true |
| namingLoadCacheAtStart | whether to read the local cache first at startup | true |
| namingCacheRegistryDir | Specify the cache subdirectory, the location is …/nacos/{SUB_DIR}/naming | empty |
| namingClientBeatThreadCount | client heartbeat thread pool size | half of the number of CPUs of the machine |
| namingPollingThreadCount | Client timing polling thread pool size for data update | half of the CPU number of the machine |
| namingRequestDomainMaxRetryCount | Number of retries requested by client to Nacos Server via HTTP | 3 |
| namingPushEmptyProtection | When the service does not have a valid (healthy) instance, whether to enable the protection, after enabling it, the old service instance will be used | false |
| push.receiver.udp.port | port of client UDP | null |
After the nacos-server@1.0.0 version, the client is supported to control some behaviors of the instance by reporting some instances containing specific metadata to the server.
| Parameter name | Chinese description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
| preserved.heart.beat.timeout | The time (in milliseconds) from healthy to unhealthy after the instance does not send a heartbeat | 15000 |
| preserved.ip.delete.timeout | The instance is deleted by the server after the instance does not send a heartbeat (milliseconds) | 30000 |
| preserved.heart.beat.interval | Interval time for the instance to report the heartbeat on the client (milliseconds) | 5000 |
| preserved.instance.id.generator | The id generation strategy of this instance, when the value is snowflake, it will increase from 0 | simple |
| preserved.register.source | Registration instance registration service framework type (such as Dubbo, Spring Cloud, etc.) | empty |
These parameters can be configured to Nacos through parameter expansion in a manner similar to namespace, such as
dubbo.registry.parameters.preserved.heart.beat.timeout=5000
4 How it works
The following is just to show the working principle of Nacos as the Dubbo registration center. It is recommended to use Dubbo Admin for Dubbo service operation and maintenance
4.1 Dubbo2 registration data
Then, restart your Dubbo application, and Dubbo’s service provision and consumption information can be displayed in the Nacos console:
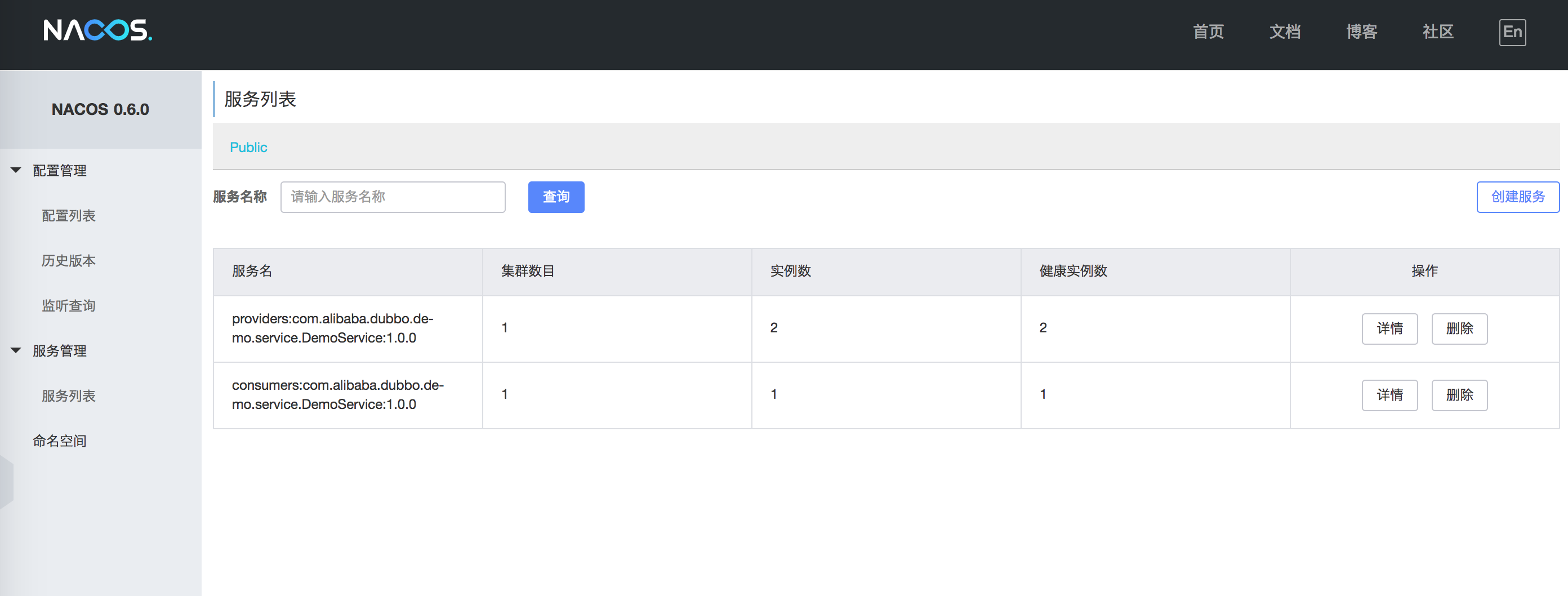
As shown in the figure, the service name prefixed with providers: is the meta information of the service provider, and consumers: represents the meta information of the service consumer. Click “Details” to view the service status details:
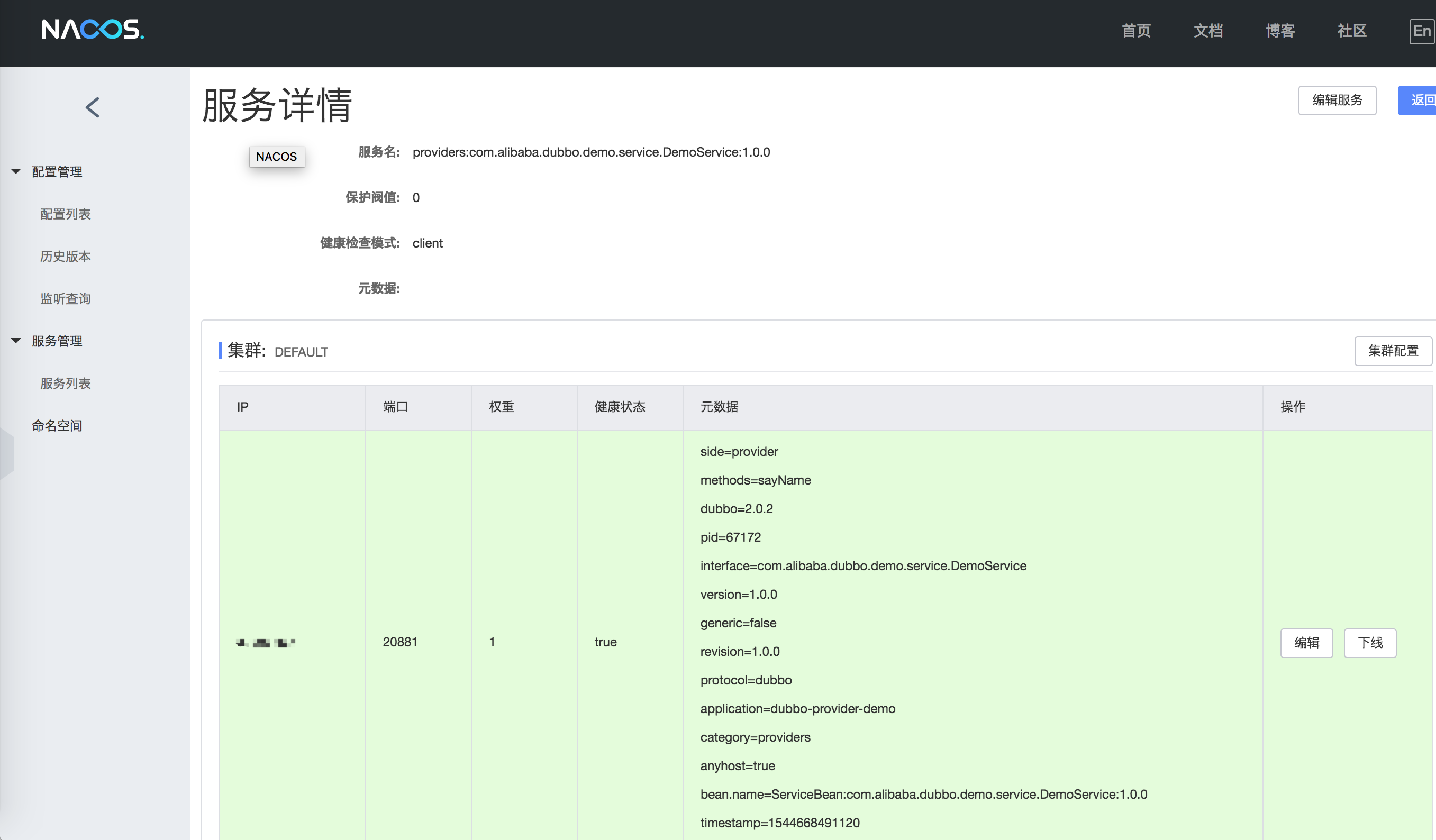
4.2 Dubbo3 registration data
The “service name” for application-level service discovery is the application name
Dubbo3 adopts the dual registration mode of “application-level service discovery + interface-level service discovery” by default, so you will find that application-level services (application names) and interface-level services (interface names) appear in the Nacos console at the same time, you can configure
dubbo .registry.register-mode=instance/interface/allto change the registration behavior.
